>>>
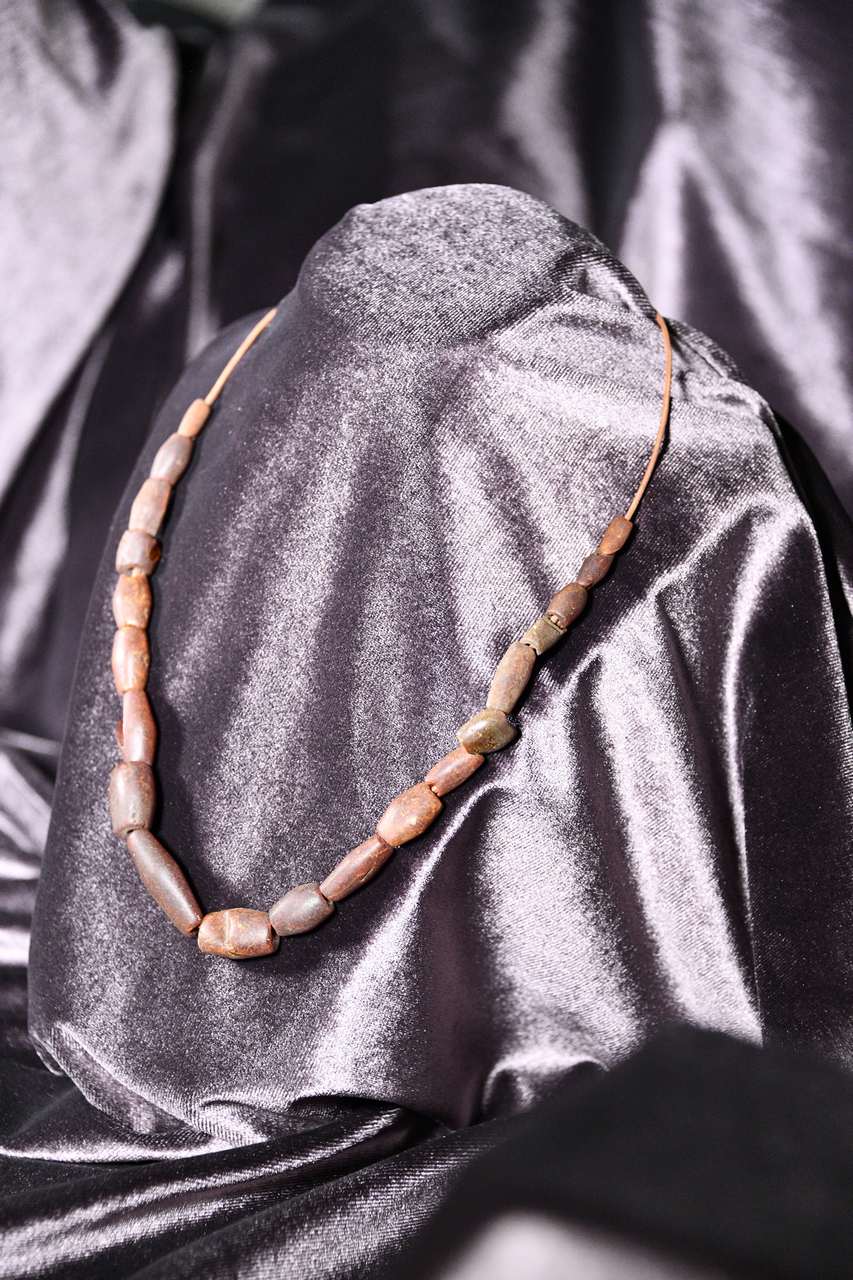

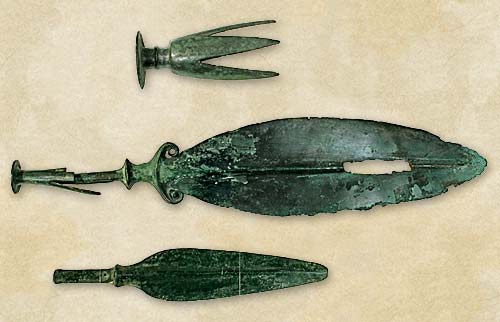
The 21 beads form part of a bronze hoard found in 2019 within a forested area close to the town of Nisporeni. Alongside the beads, the hoard included numerous bronze ornaments (2 Röschitz-Sanislău-type fibulae, 7 necklaces, 12 rings, 22 tubes, 23 bracelets, and approximately 80 appliqués), one coral bead and a pendant made from a wild animal's tooth. At present, the amber beads are preserved in the collections of the Muzeul Național de Istorie a Moldovei, while the remainder of the hoard is in the possession of a private collector.
The hoard was discovered accidentally in a pit about 50 cm deep. The objects in this hoard are of Western origin, with known parallels in archaeological complexes from Poland, Hungary, Serbia, and Slovakia, and, to a lesser extent, in Romania. The presence of this bronze hoard on the territory of the Republic of Moldova illustrates the cultural dynamics of the region during the Early Iron Age and a fundamental shift in the vector of cultural influences from east to west.
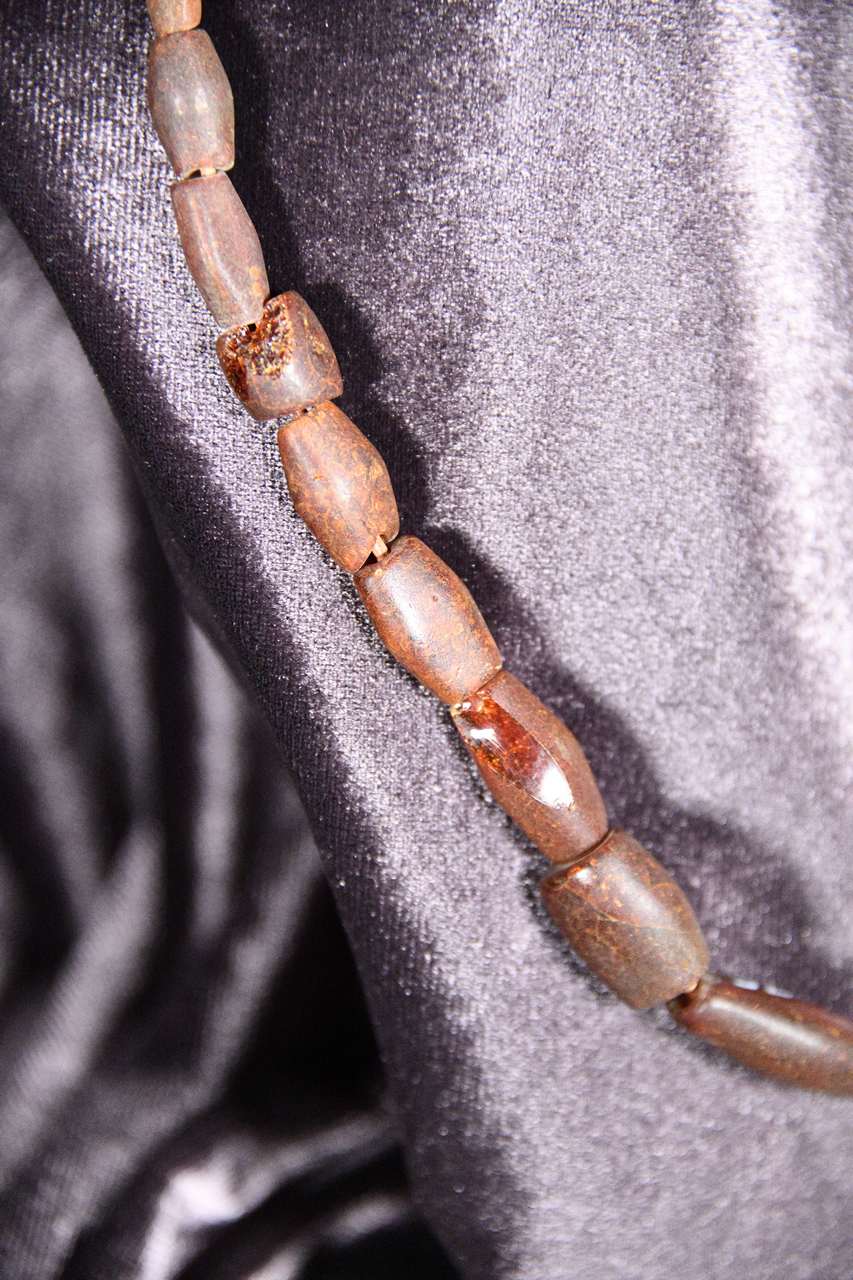

The amber bead strand comprises 16 whole beads and five fragmentary ones. They have an elongated biconical shape and vary in size. The beads are brown-reddish in color; their lengths range from 1.1 to 3.1 cm, widths from 0.6 to 1.4 cm, thicknesses from 0.6 to 1.1 cm, and the perforation diameter ranges between 0.2 and 0.3 cm.
Amber beads appear in several bronze hoards dated to the Late Bronze Age in the eastern half of Slovakia and in Transdanubian Hungary. Parallels are also known from the Cioclovina Cave in Romania. With the onset of the Iron Age, amber items disappear from the Carpathian Basin for approximately 300 years, reappearing alongside the arrival of Scythian elements.
The bronze hoard discovered at Nisporeni is dated to the HaA2-HaB1-2 interval (1050/1000 - 800/750 B.C.).