>>>

Christmas bells entered the Romanian cultural space through a long process in which archaic traditions blended with Christian belief and European influences. Long before the holiday of Christmas developed as we know it, metallic sounds played an important ritual role in old communities: they were used to drive away evil spirits, to purify spaces, and to protect people during transitional moments at the turn of the year. These beliefs have been preserved in winter customs such as caroling, the Plugușor, and masked dances, where bells and jingles were indispensable.
With the spread of Christianity, the sound of the bell also acquired a profound religious meaning, becoming an announcer of major feasts and a symbol of the Nativity. Small bells, however, were not originally used as decorations but primarily as functional or ritual objects.
The first decorated Christmas tree in the Romanian lands was the one at the palace of Prince Carol I of Hohenzollern, following his arrival in the Romanian Principalities in 1866. From that moment the tradition took root, and on Christmas Eve princes and princesses invited to the palace would take part in decorating the tree. Among the ornaments used were small metal bells, symbolizing joy, the good news, and divine protection for the home.
In the twentieth century, Christmas bells spread across all Romanian provinces and became a visual emblem of the holiday, appearing in both decorations and carols. Even during periods when religious expression was curtailed, bells remained in people's homes as signs of joy and the continuity of tradition. Today they retain this dual meaning: the echo of ancient beliefs and, at the same time, the announcement of the Birth of Christ - a symbol of hope, light, and the link between past and present.
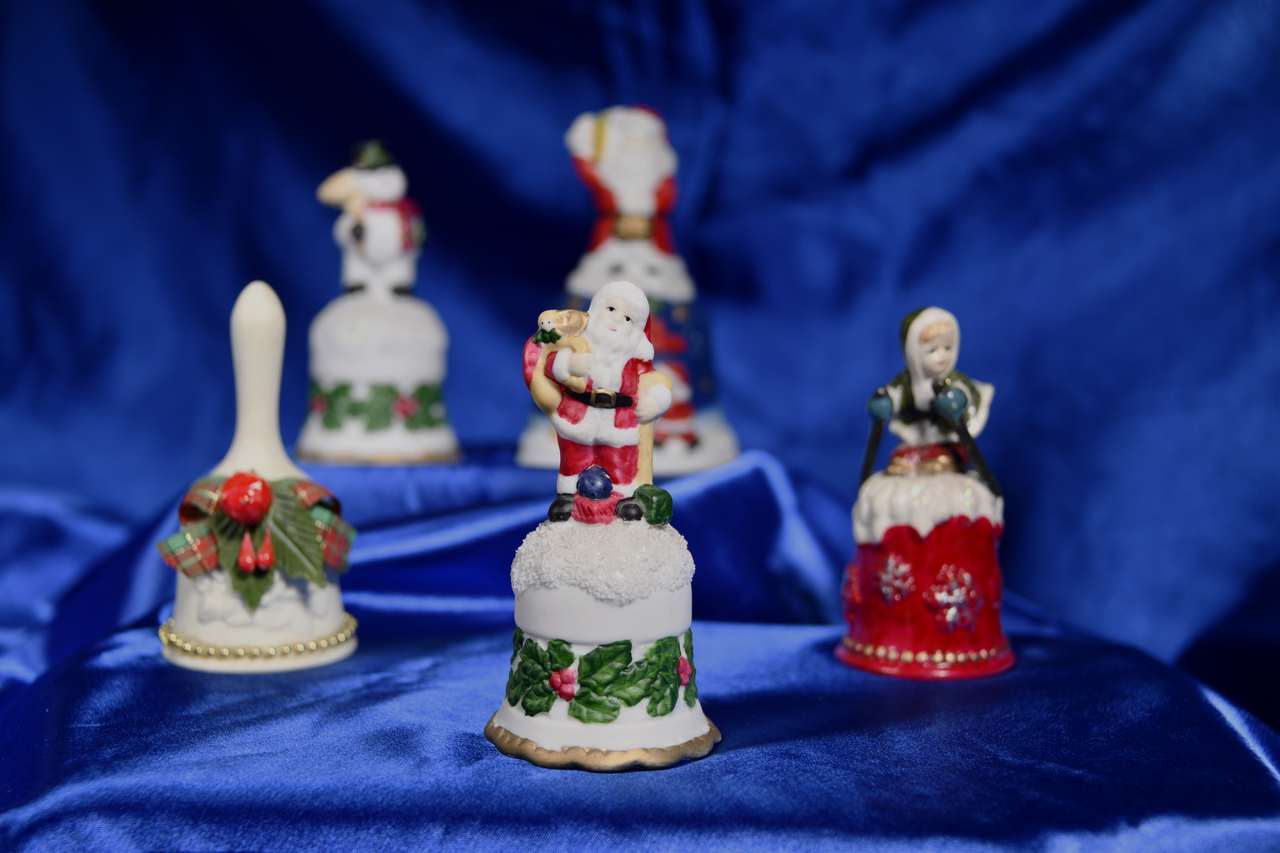
These tinkling pieces are part of a generous heritage collection at the National Museum of History of Moldova (NMHM), which includes more than 200 cultural items. A substantial contribution to the museum's collection of decorative bells was made by Dorina Raischi, a teacher at School No. 94 in Chișinău, who donated 174 bells, of which around 30 are winter-themed. Made of ceramic, porcelain, glass, and metal, they were brought from different parts of the world and together offer a succinct picture of the global culture of bells. They add a festive note to the home and even to a gift, and it is hard to imagine Christmas without their cheerful tinkling.




 31 August 1989 St., 121 A, MD 2012, Chisinau, Republic of Moldova
31 August 1989 St., 121 A, MD 2012, Chisinau, Republic of Moldova